SQL Server Agent jobs are needed for automating tasks such as backups, index maintenance, and data processing.
This post provides a SQL script to list all SQL Server Agent jobs on an instance, along with useful tips to help understanding.
How to List SQL Agent jobs in SQL Server
The following query retrieves all SQL Agent jobs, including job steps and key details:
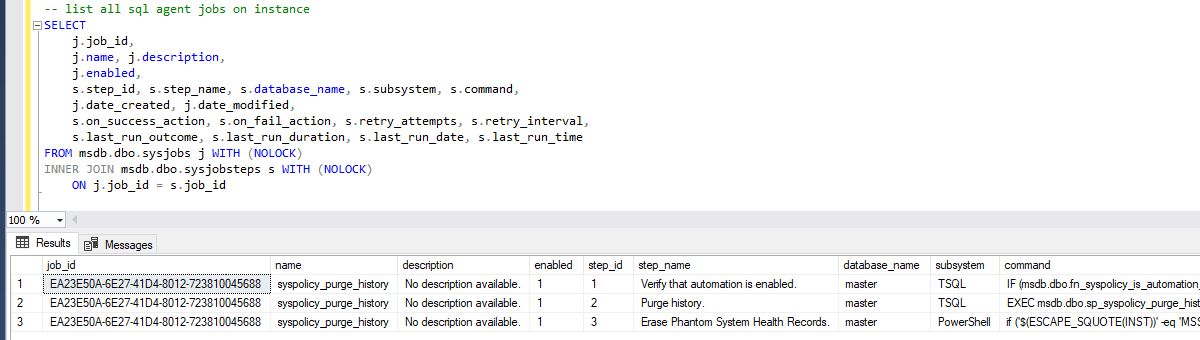
This query provides a clear view of SQL Agent jobs, including their status, execution history, job steps, and scheduling details. You can quickly determine if a job is active, when it last ran, how long it took, and whether it succeeded or failed. Additionally, it reveals the steps within each job, their execution context, and any retry settings. Scheduling details help you understand when and how often a job is set to run.
✅ Key Details
– Job Overview: Name, description, status (enabled/disabled), creation date, and last modified date.
– Execution History: Last run date/time, run outcome (success/failure), and execution duration.
– Job Steps: Step name, database context, command, and retry behavior.
– Schedule Information: Schedule name, frequency, interval, and start time.
📖 For more details, refer to MS Docs:
📌 sysjobs | 📌 sysjobsteps | 📌 sysschedules
Retrieve Only SQL Agent Jobs (Excluding Steps)
If you only need a list of jobs without step details, simply query the table as linked above:
This returns one row per job, helping you quickly review job configurations.
Tips for Managing SQL Agent Jobs
Here’s how you can make your SQL Agent job management easier:
> Use Descriptive Names & Tags:
Clearly name jobs to reflect their purpose and consider using standardized prefixes (e.g., DBA_, ETL_, Backup_) to improve job organization. Add detailed descriptions where appropriate.
> Monitor & Alert on Failures:
Regularly check for failed executions to ensure reliability. Set up Database Mail (DBMail) or a customized alerting solution to notify DBAs instantly when a job fails.
> Optimize Scheduling & Performance:
Avoid scheduling multiple resource-intensive jobs simultaneously. Use job history’s run_duration to analyze and optimize job execution times, preventing overlaps and performance bottlenecks.
> Backup Job Configurations:
Before making changes, export job details using sp_help_job, PowerShell, or custom scripts to ensure you can quickly restore them if needed.
Hope all this was useful for you!
Leave a Reply