Git log is an essential command when working with git version control. It allows you to see the history of a repository, including details about each commit like the author, date, and commit message. It lets you know what’s changed, when it changed and by who.
In this post I’m sharing some examples of using the git log command to help get you started.
Basic Git Log Example
Using the git-log command is simple:
$ git log
his will display a list of most recent commits in your repo, starting with the most recent
Git Log Parameters & Options
The git log command has several options that allow us to tailor the information it displays. For instance, you can use it with the –oneline parameter to condense results, or with the –auther paramter to filter results by user.
We can also change the output format:
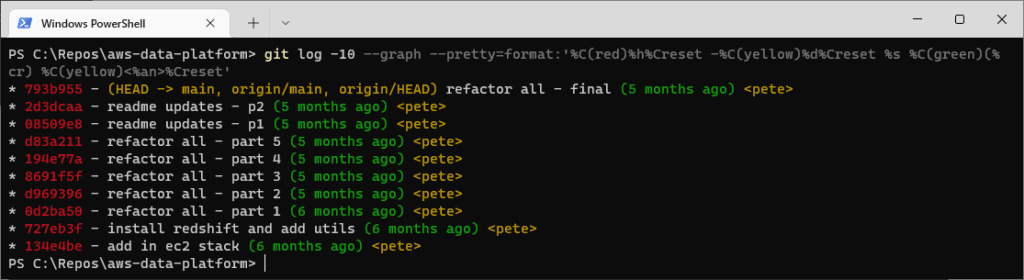
# show most recent 5 commits on one line, with formatting git log -5 --graph --pretty=format:'%C(red)%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %C(green)(%cr) %C(yellow)<%an>%Creset'