This post contains a demo installation of Active Directory Domain Services on Windows Server 2016. It follows a previous post for a series of test lab configuration posts.
Microsoft docs on installing AD on Windows Server can be found here: Install Active Directory Domain Services
Configuring a Windows Server 2016 on a local Hyper-V can be done by following my previous post: Installing Windows Server 2016 with Hyper-V
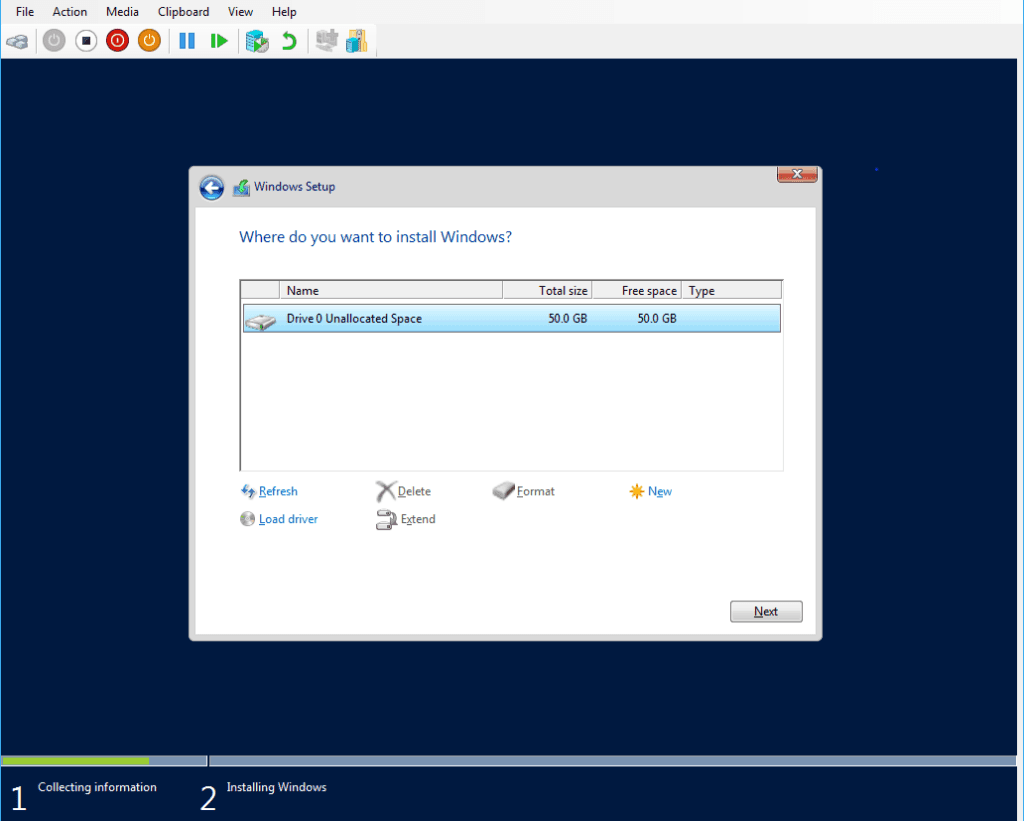
The following steps will get your test Windows Server environment set up to run Active Directory:
# Create a Hyper-V Private Network.
# Configure Windows TCP/IP Settings.
# Rename the Windows Server Host.
# Install Active Directory.
# Promote the Server to a Domain Controller.
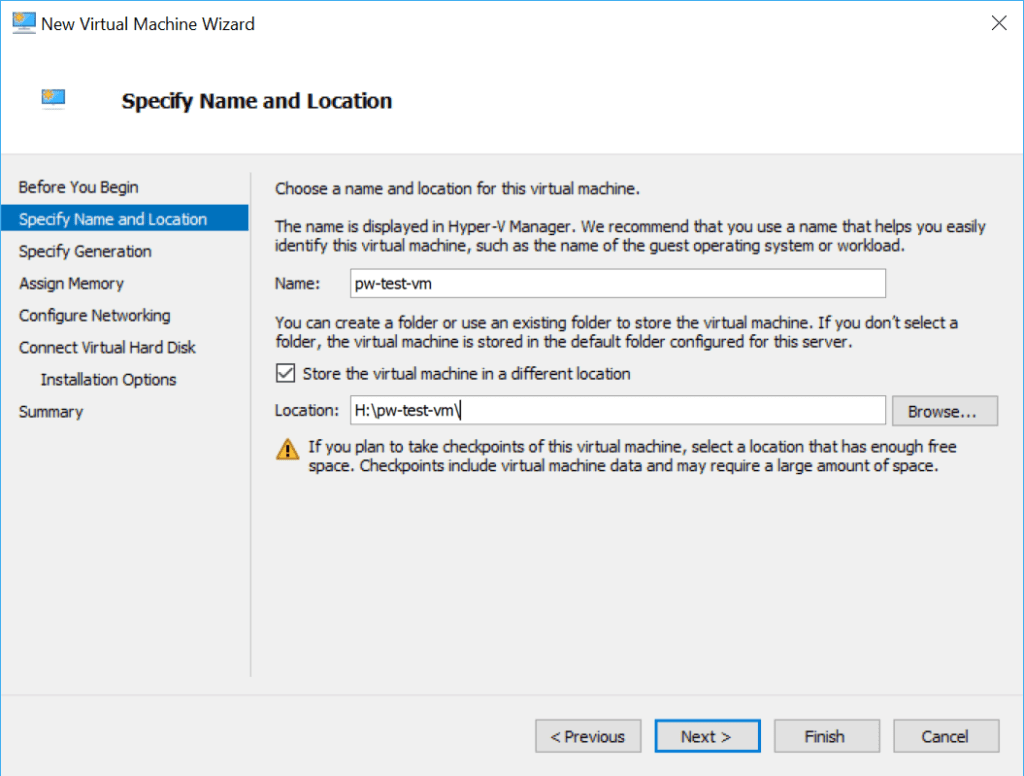
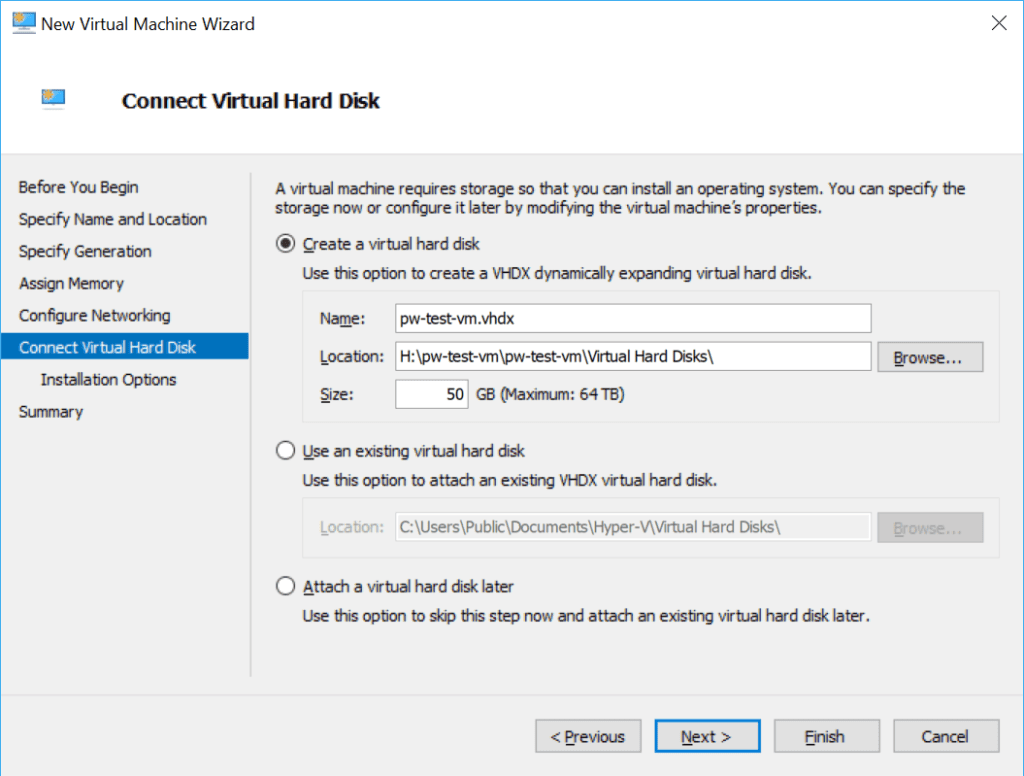
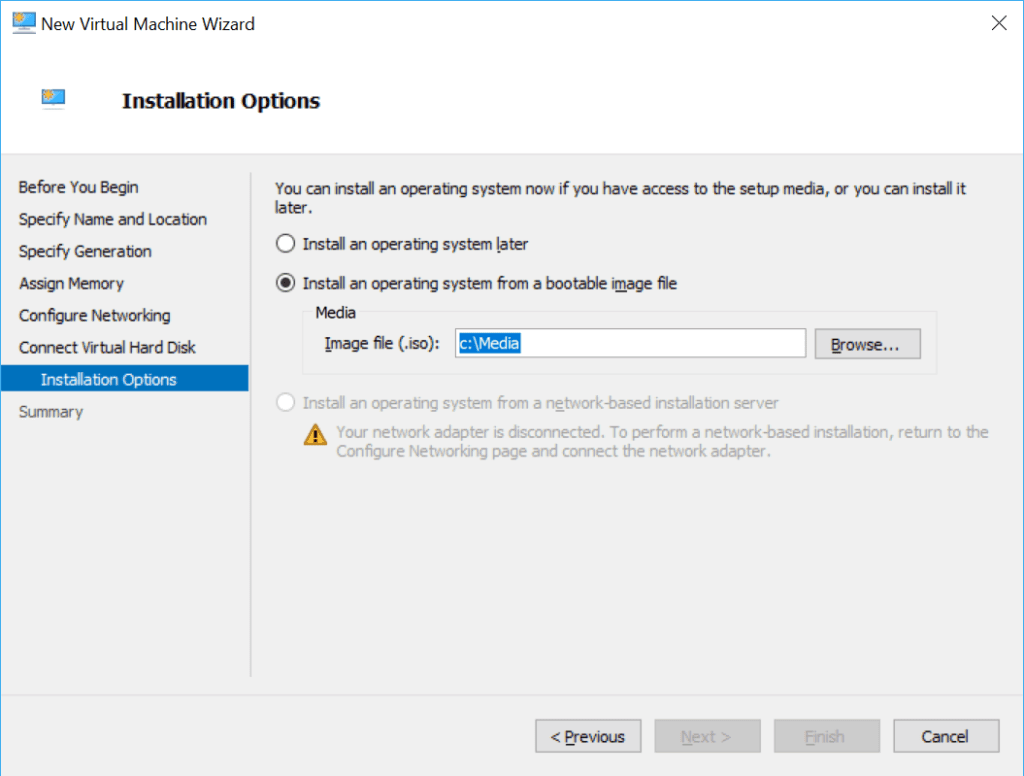
Once the above has been achieved, you can create a new VM in Hyper-V (or other Hypervisor) and join your Domain, as I’ve done for some tests.
Create a Hyper-V Private Network
1. Right-click the Hyper-V host and select Virtual Switch Manager.
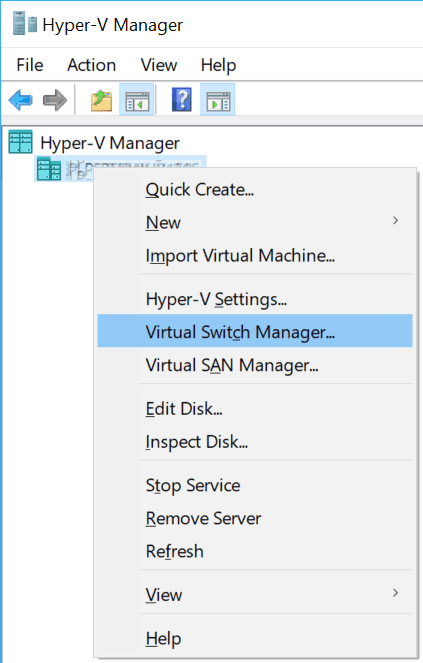
2. Select Private and Create Virtual Switch.
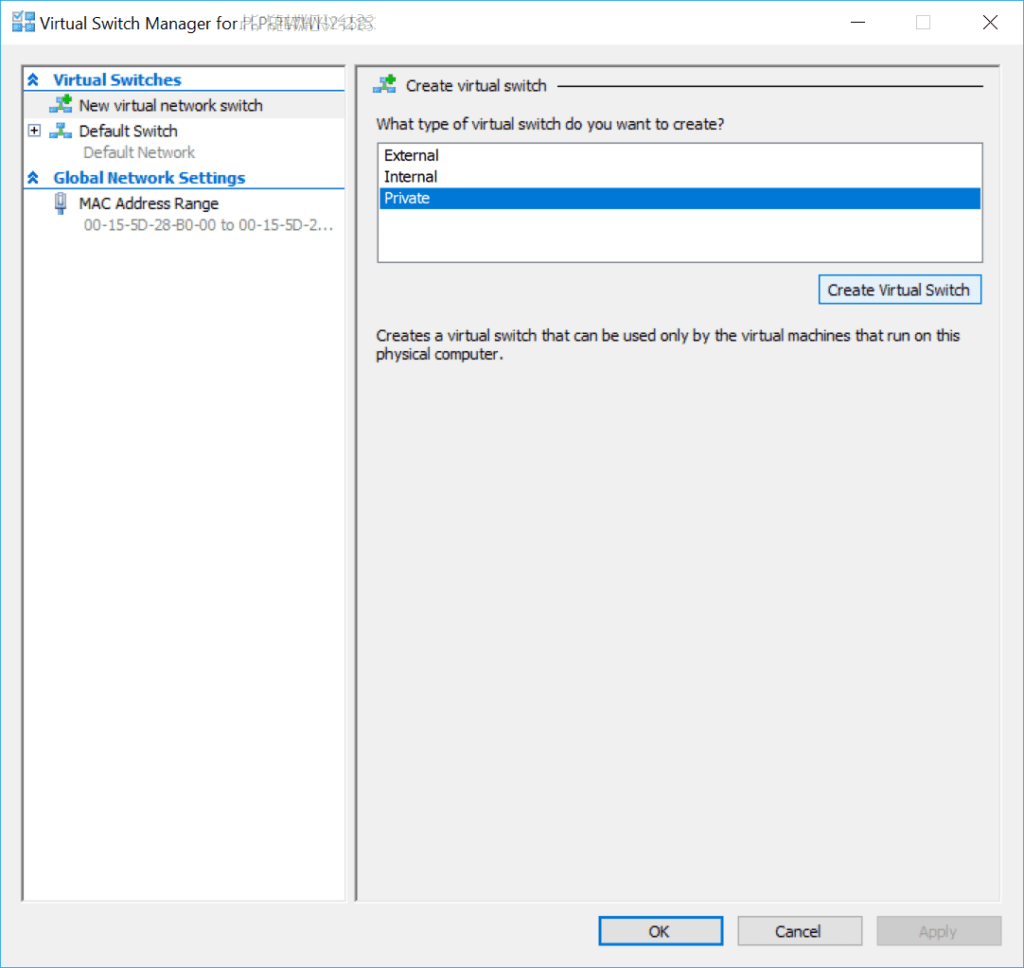
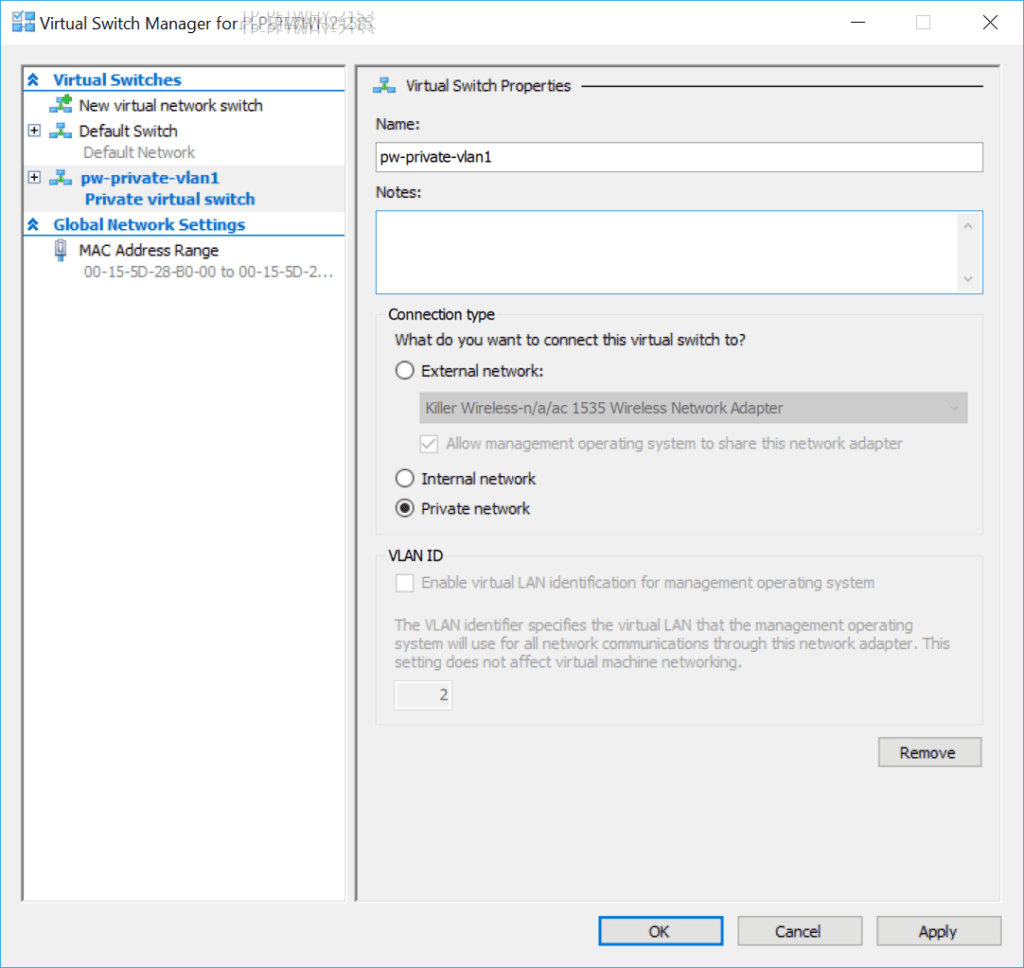
3. Enter a name for the network and click okay.
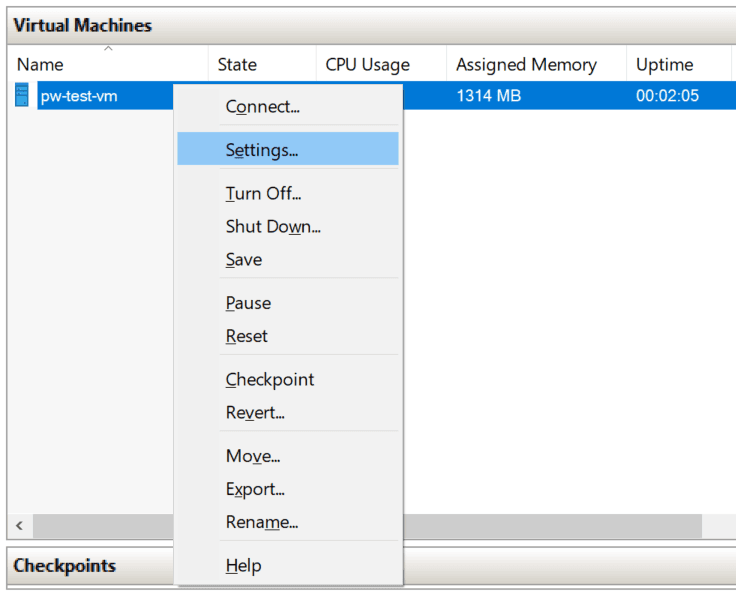
4. Right-click the VM in Hyper-V and click Settings.
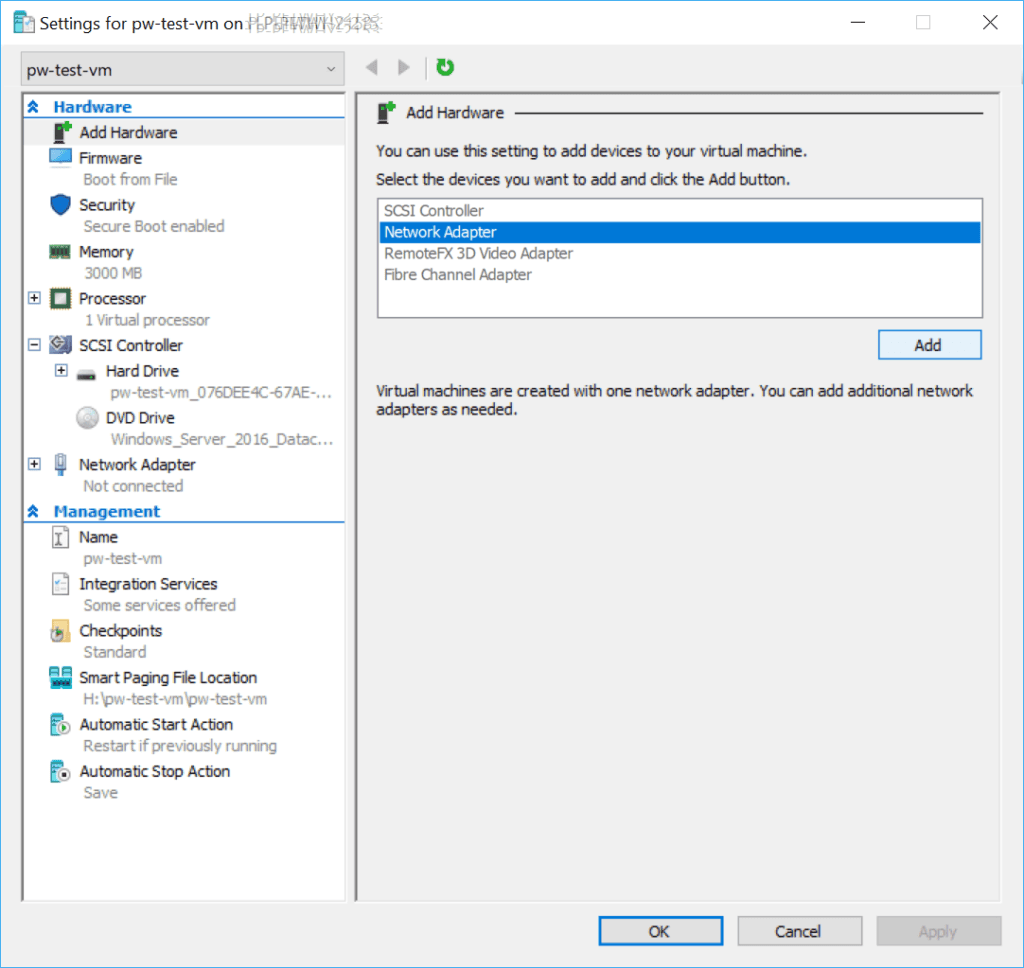
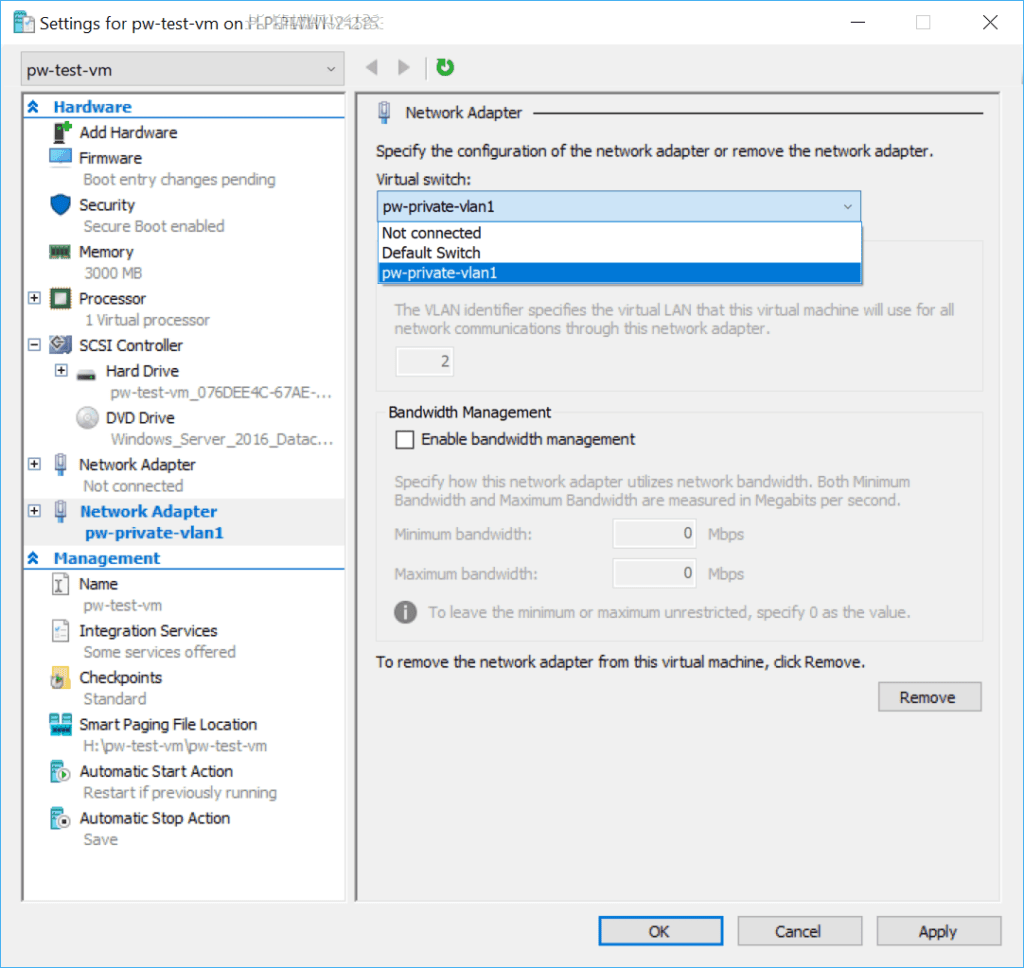
5. Add a new Network Adapter.
6. Select Private vSwitch as named above and click OK.
Configure Windows TCP/IP Settings
1. When the above has been set-up, Windows Server will show network settings as Identifying…
2. Right-click the network icon and click Open Network and Sharing Center.
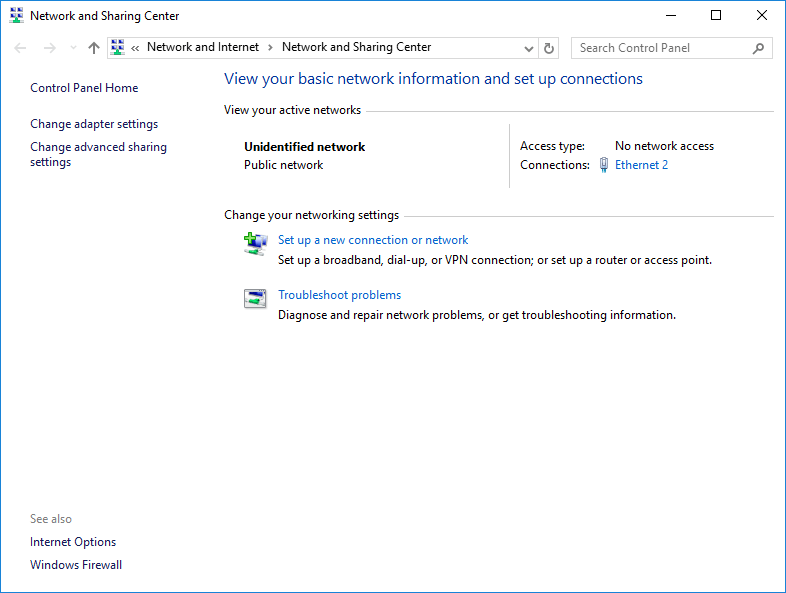
3. Click the highlighted active Ethernet connection.
4. Open Properties.
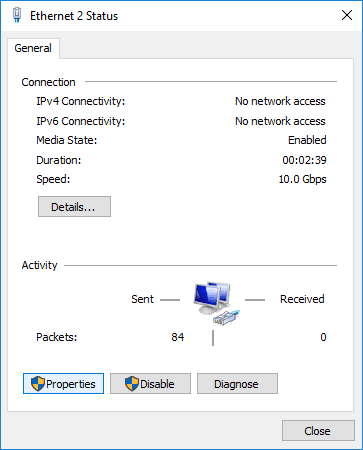
5. Open Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties.
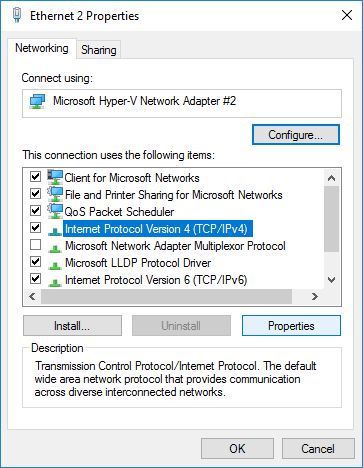
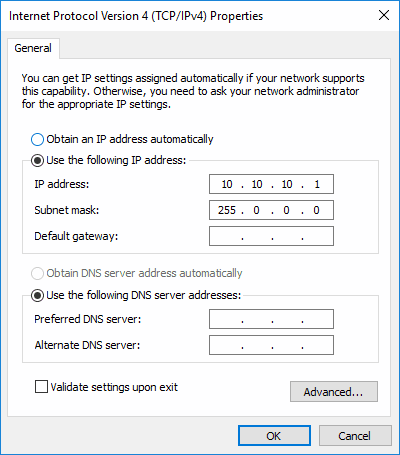
6. Enter IP and subnet addresses.
Rename the Windows Server Host
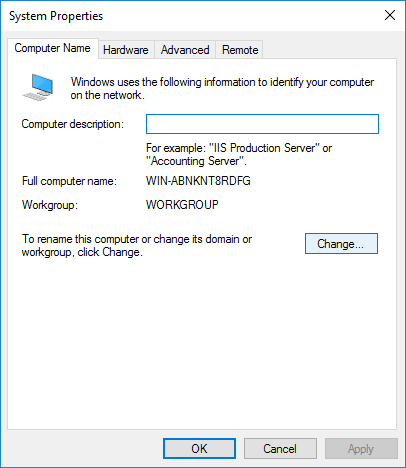
1. Open Server Manager and click the highlighted Computer Name.
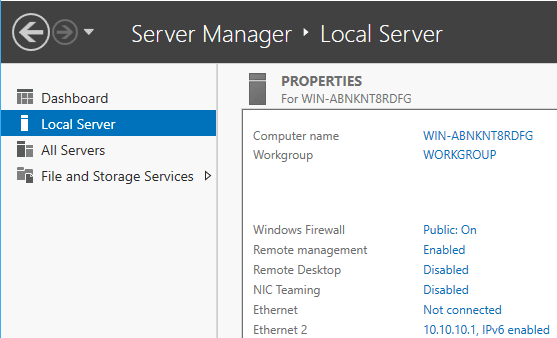
2. Click Change…
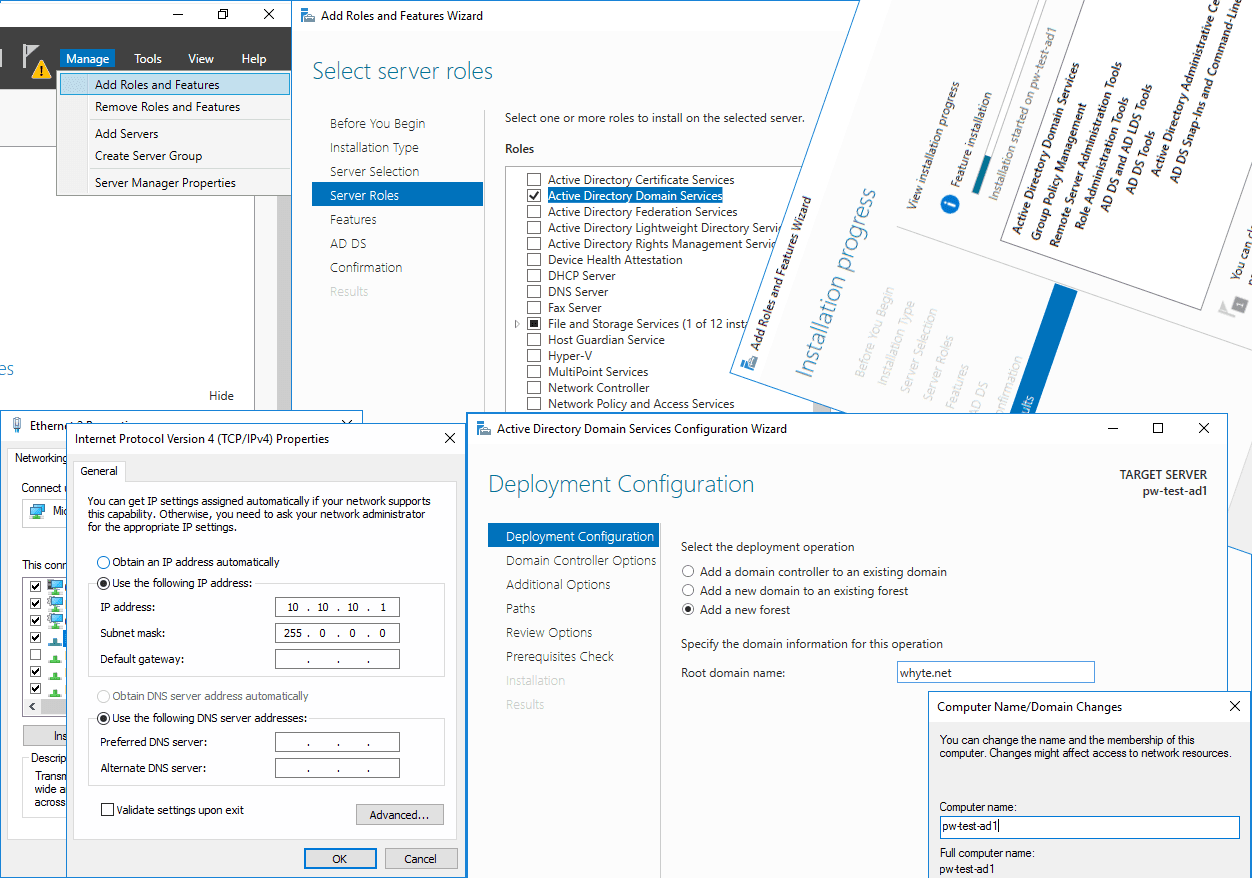
3. Enter new Computer Name and click OK.
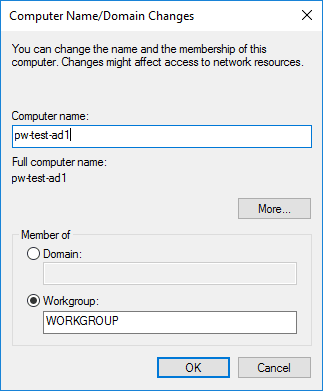
The host will require a reboot once done.
Installing Active Directory
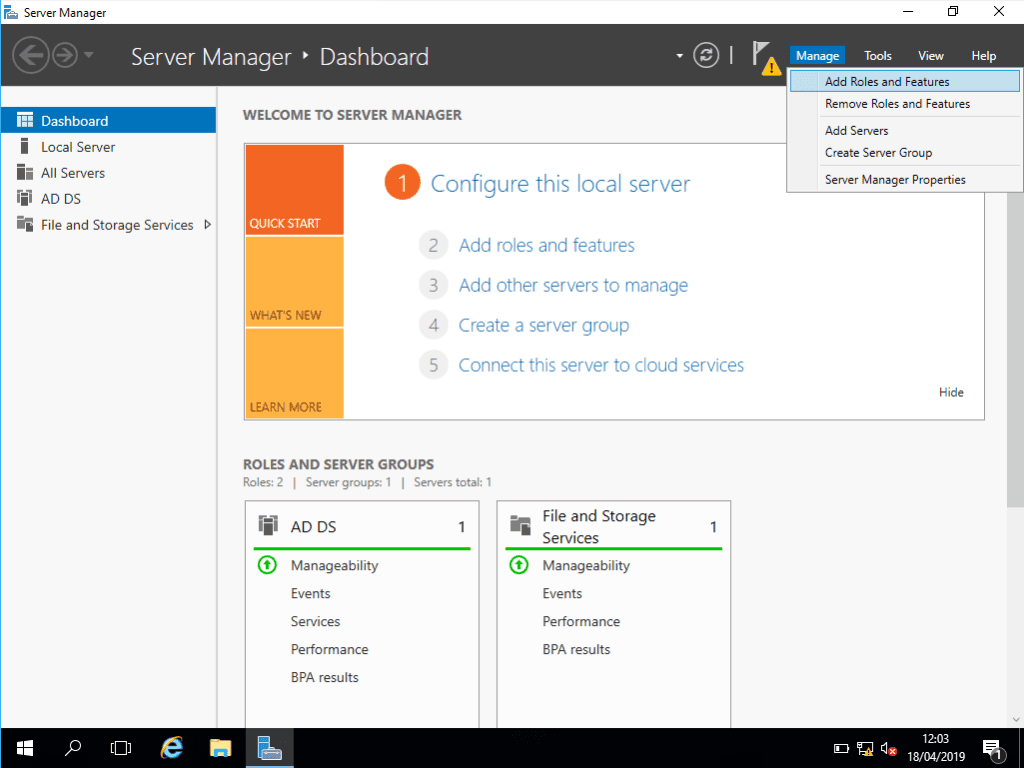
1. Within Server Manager, click Manage > Add Roles and Features.
2. Before you begin, read the before you begin.
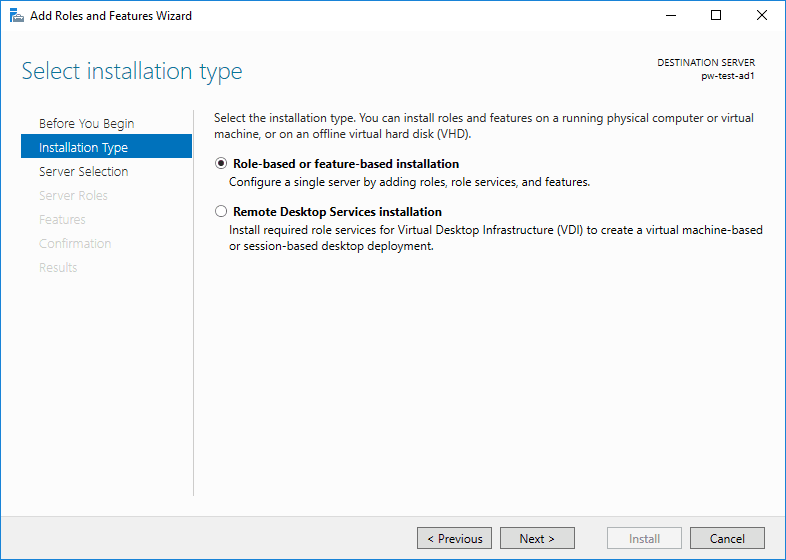
3. Select Role or Feature-based installation.
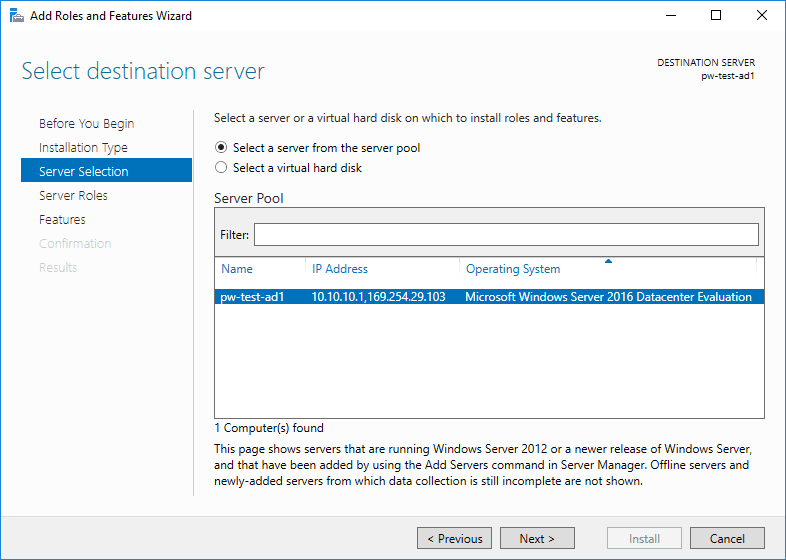
4. Select the destination server.
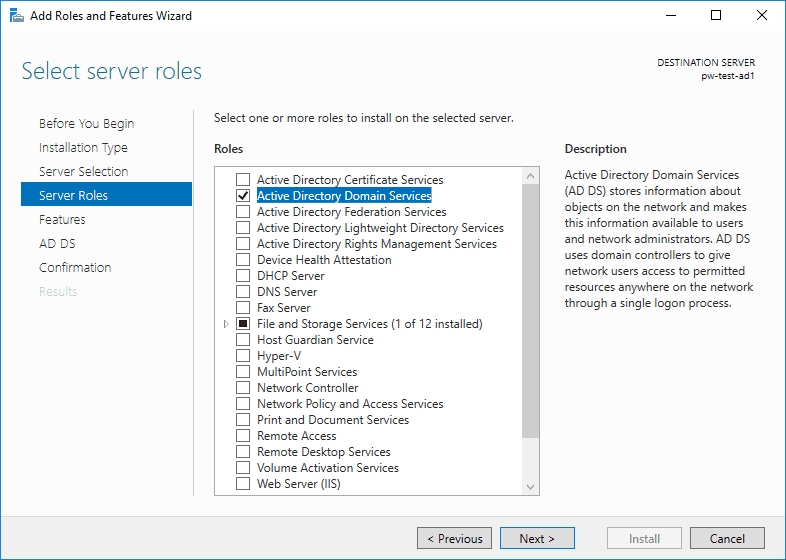
5. Tick the Active Directory Domain Services checkbox.
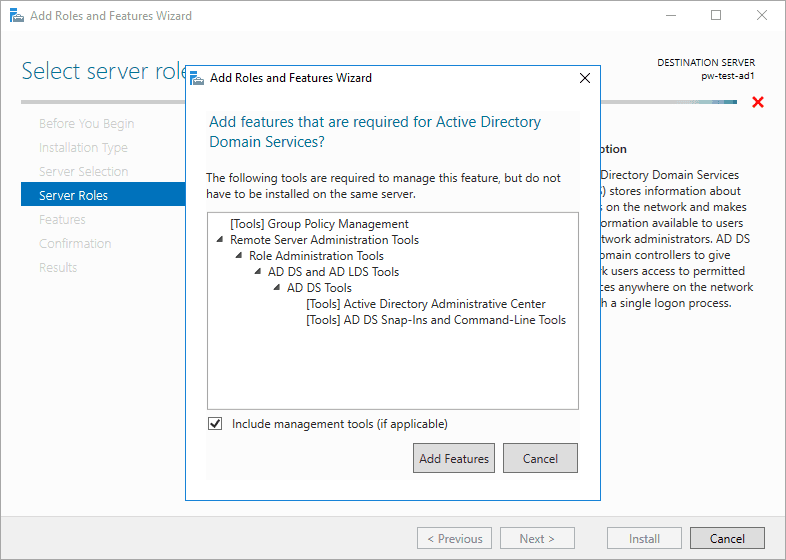
6. The following will appear – click to add the additional tools.
7. No features are being added at this time – click to continue.
8. ADDS page is worth a read – nothing to change here.
9. Review and click to install.
10. Leave it a few minutes and we’re then able to promote this server as a new Domain Controller.
Promote the Server to a Domain Controller
1. Once done with the above, there won’t be a finish point within the wizard. Click the flag on Server Manager to Promote the server to a Domain Controller.
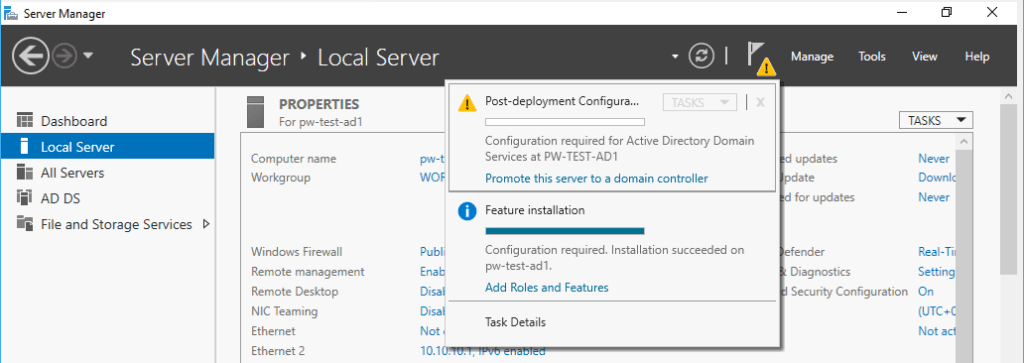
2. This is a new test environment, so I need to Add a new forest.
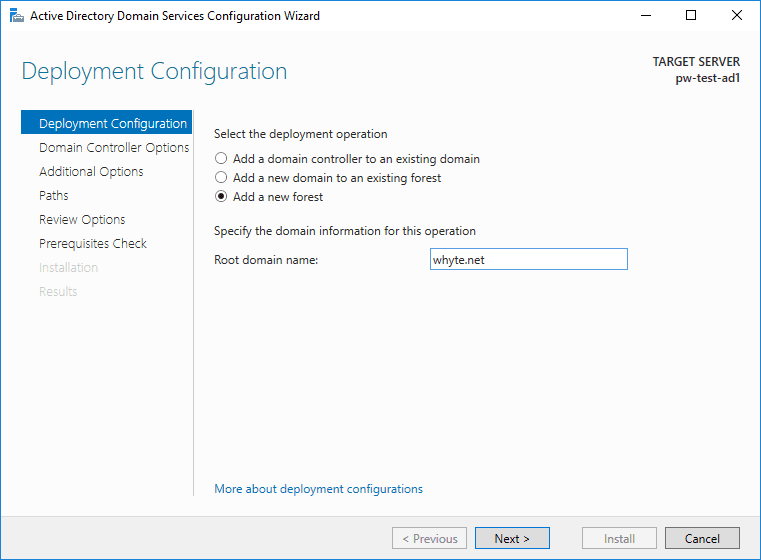
3. A new Forest means Functional Levels can be the latest edition available, Windows Server 2016. This is also the place to enter an important password that is required if recovering a failing AD.
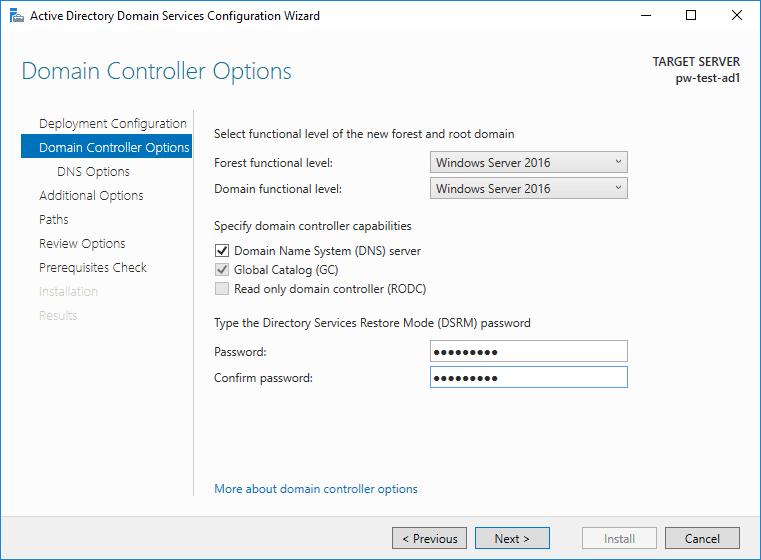
4. The following error is listed within the known issues for installing and removing AD DS. It’s expected if create a new forest as I’m doing.
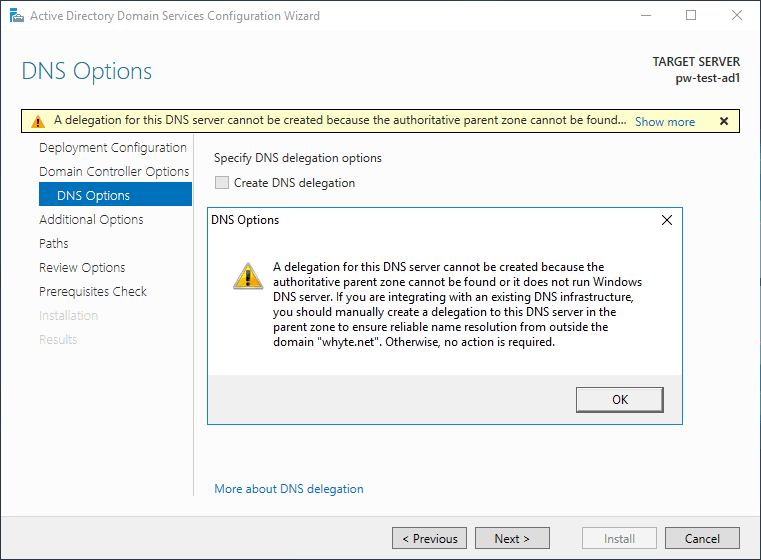
5. Enter a preferred NetBIOS name.
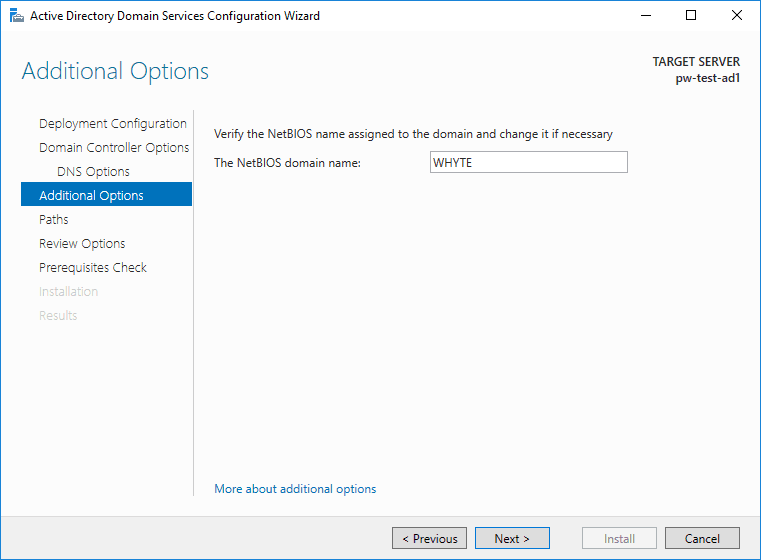
6. Locations can stay as defaults of course.
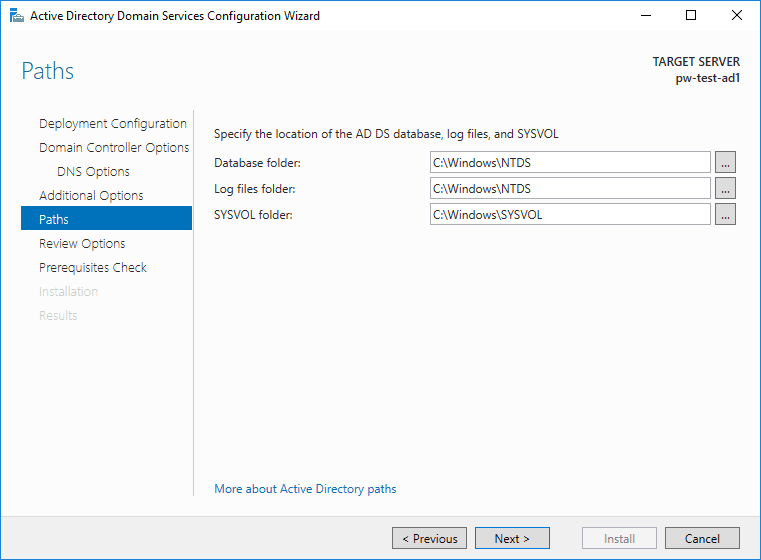
7. Time for us to review wizard selections.
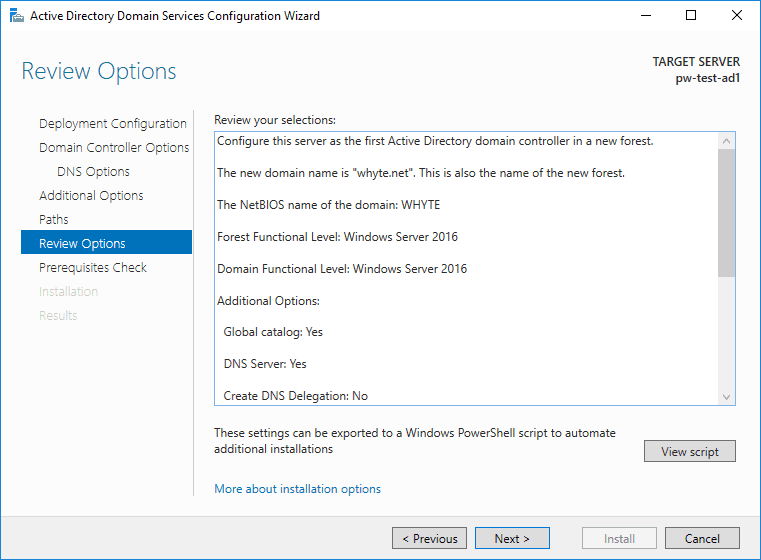
8. As you’ll see in the image above, we can click to view the PowerShell script that is about to run with the wizard selections included.
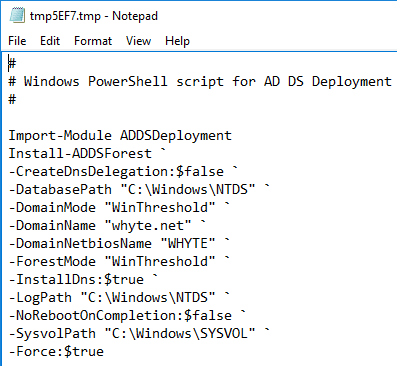
9. A prerequisites check will run as we hit next from above.
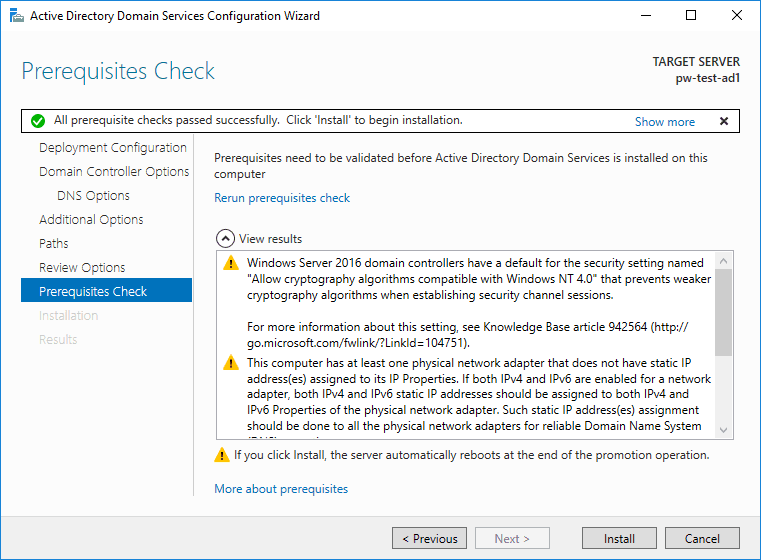
10. Click to install…
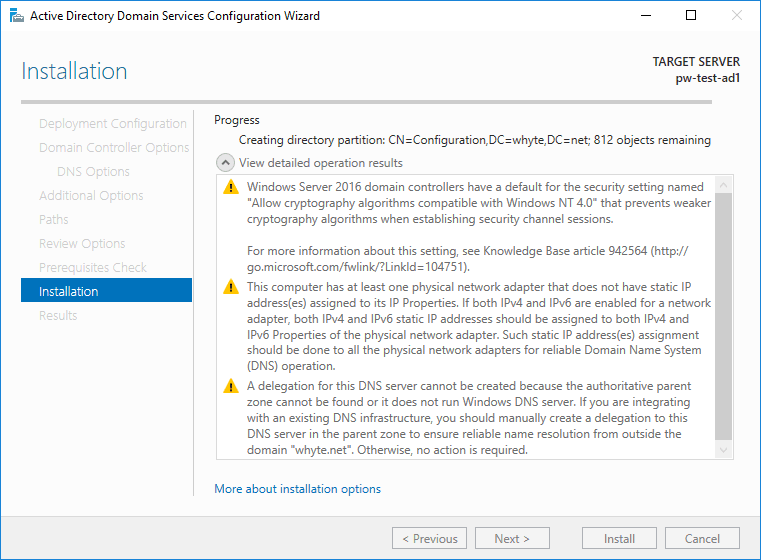
11. An automatic reboot will be initiated at the end.
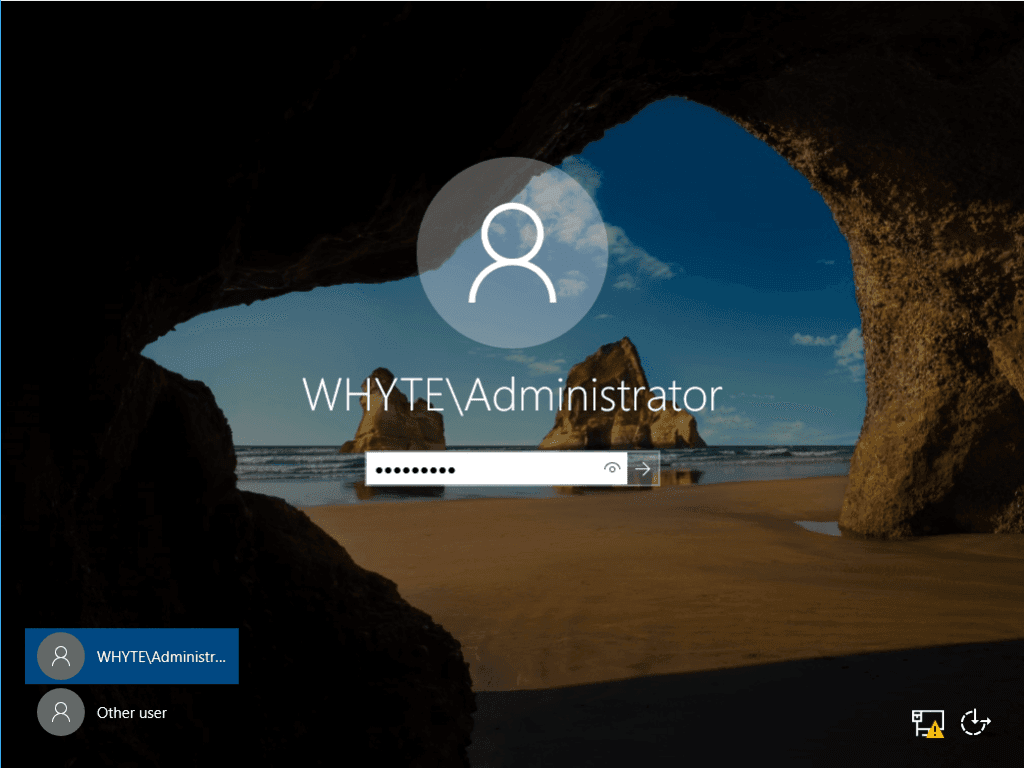
12. When back up and running, we can log in to the new domain.
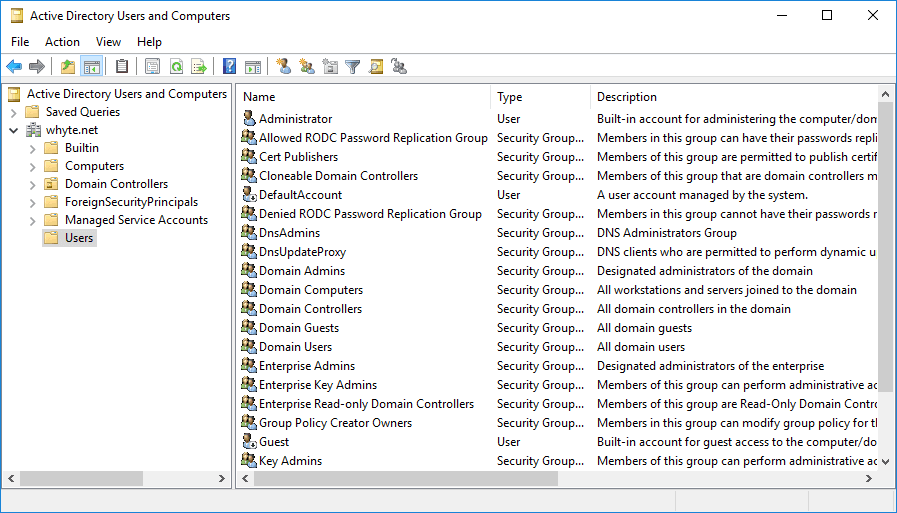
13. And have a look at our Active Directory Users & Computers, just for the fun demo of course.