Linked Servers in SQL Server allow you to query external databases, such as remote SQL Server instances, Oracle, ODBC or MS Access databases. It provides easy query access to another database server for users, however it’s not the most efficient ways to do it.
The following steps should help walk you through creating a Linked Server to another SQL Server:
> 1, Test Connectivity to the Remote Server
> 2. Create a SQL Login for Linked Server
> 3. Create a Linked Server to SQL Server
1. Test Connectivity to the Remote Server
An important step before we begin the SQL Server configuration, we need to confirm we have line-of-sight to the remote server. On this local setup, I have nothing to worry about, it’s localhost\sql-instance01 connecting to localhost\sql-instance02.
The network information we’ll need for this includes:
– Remote Server Address (IP Address or FQDN)
– Port Number (The SQL Server default port is 1433)
Once you have this info, amend the following Test-NetConnection cmdlet and run it:
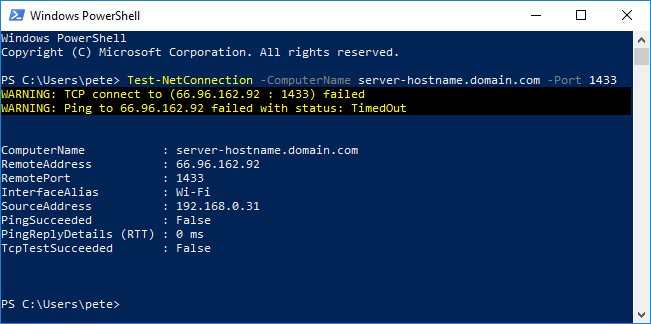
In this example, both the Ping and TCP tests are succeeding. You’ll find that it has a delay when failing, maybe it’s 30 seconds.
If it fails, you’ll have to review things like the Local Firewall Rules, Security Groups, and External Firewalls (contact the network folks).
If using Windows 8 / Windows Server 2012 or Older:
Use the script in this other blog post, or if you’d like to see some added info on this.
Here’s some other note-worthy default database server ports to have as a note:
– PostgreSQL (5432)
– MySQL (3306)
– Oracle (1521)
– Sybase (5000)
– DB2 (50000)
2. Create a SQL Login for the Linked Server
We’ve verified we have network connectivity to the remote server, now we need to create a SQL login for the Linked Server.
We need a new user on the server we’re linking to. I’m using my PETE-PC\SQL2019 SQL Instance as my main server, creating the new login on the PETE-PC Named Instance below: .
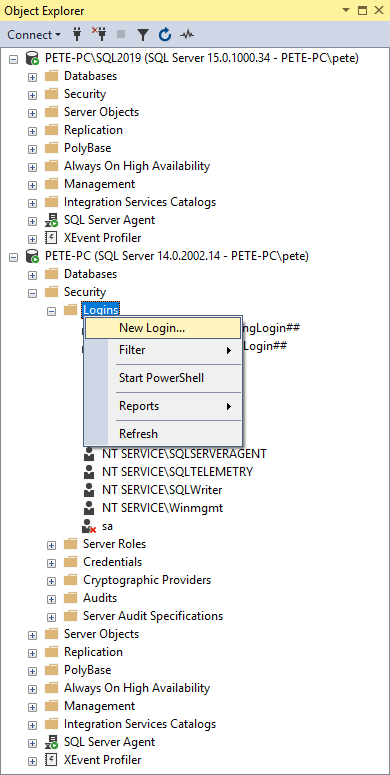
Select SQL Server authentication:
Set the required permissions.
For this example I only need read access, so I’ll select db_datareader on the database:
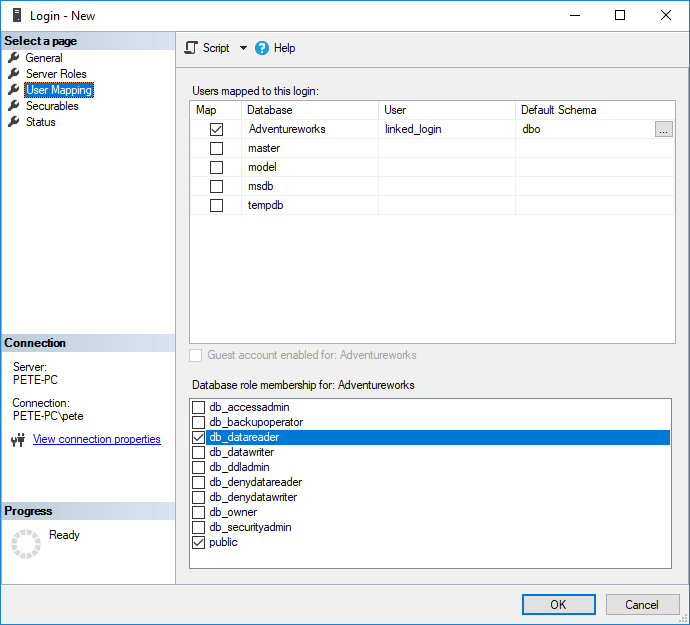
Once you have this set you can click OK and proceed to the next steps.
3. Create a Linked Server to SQL Server
To create a Linked Server to another SQL Server:
1. Open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and connect to your server,
2. Expand Server Objects.
3. Right-click Linked Servers.
4. Select New Linked Server.
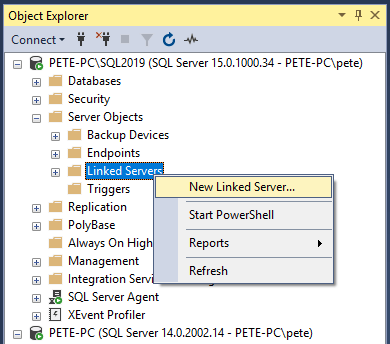
5. A New Linked Server window will prompt.
Select SQL Server as the server type and enter the the remote SQL Server Name.
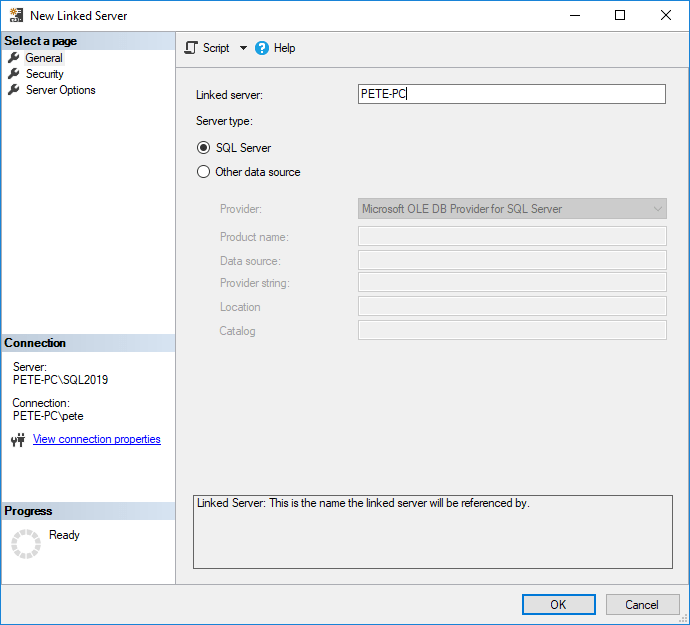
Into the Security tab next, enter the remote login details (as created above).
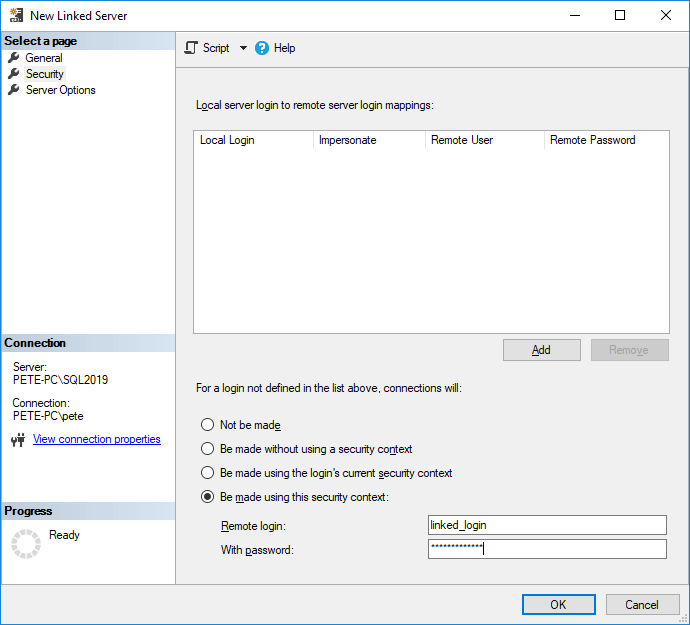
6. Click OK to confirm.
We can also script this configuration out to a T-SQL query window before running it.
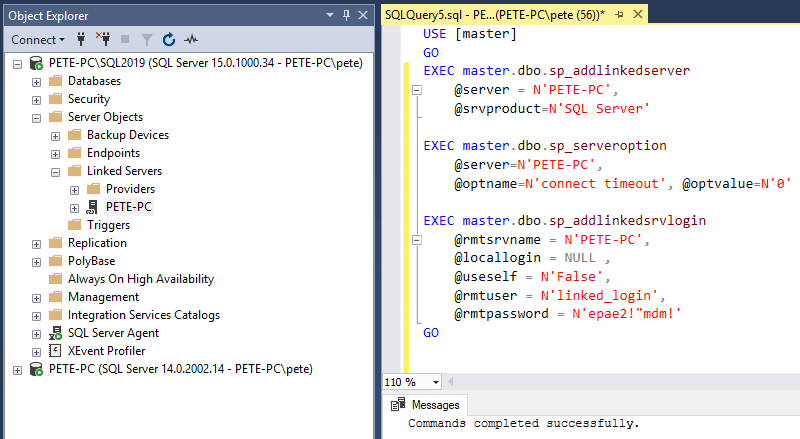
To create this Linked Server it’s using the following Stored Procs:
> sp_addlinkedserver
> sp_serveroption
> sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
7. Verify Linked Server.
We can verify the link by querying the new Linked Server Database:
-- query linked server database SELECT * FRMO [linked-server-name].[database-name].[schema-name].[table-namme];
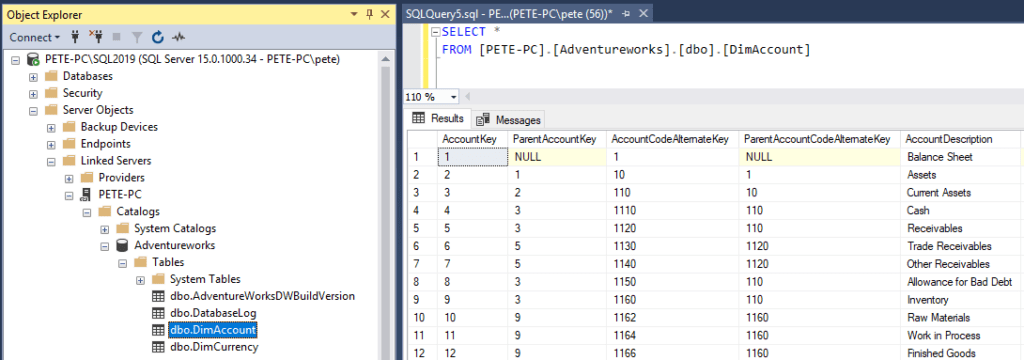
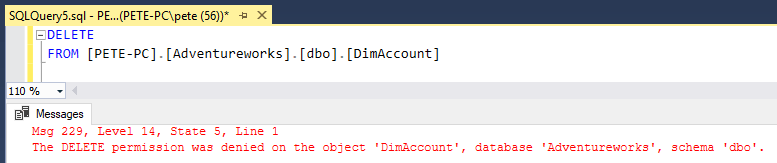
8. And finally, as a DBA we should be verifying permissions:
Leave a Reply