Accessing local Windows files from a WSL distribution allows integration between workflows, our local Windows environment and (WSL) Linux environments.
This is done by navigating to the /mnt/c/ directory within your WSL Linux terminal.
Alternatively, you can enter WSL directly from any Windows directory using a terminal. Both approaches provide straightforward ways to integrate your workflows across both platforms.
Additionally, for more advanced workflows, you can create a symbolic link between Windows and WSL directories. Check out my other post, Create a Link Between Local Windows Files and WSL, for a detailed guide.
Navigate in Terminal to /mnt/c/
In a WSL environment, Windows drives are mounted under the /mnt/ directory. For example, the C: drive is accessible at /mnt/c/.
Here’s how you can navigate and interact with local Windows files:
# navigate to home (wsl) linux folder cd ~ # navigate c:\temp folder on local windows computer cd /mnt/c/temp
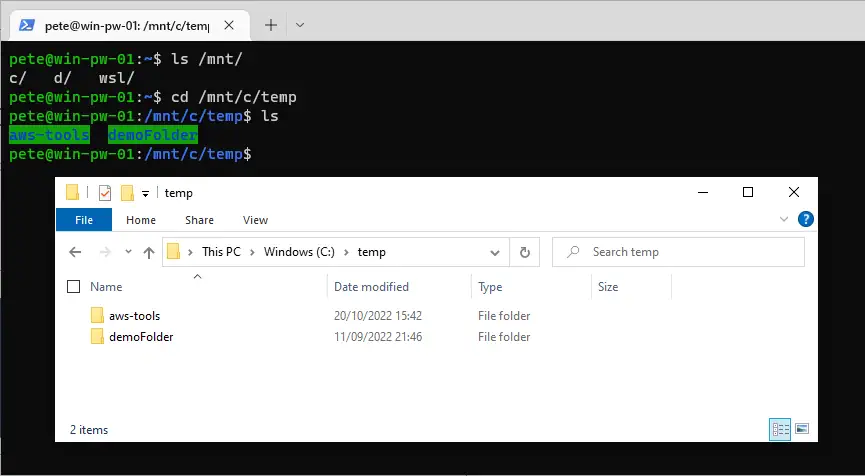
In the example above, we accessed the C:\temp folder from within the WSL environment. The /mnt/ directory reflects the local Windows drives, allowing you to browse and manipulate files seamlessly.
Open WSL from PowerShell with a Specific Directory
You can also launch WSL directly from a PowerShell terminal while being in any Windows directory.
This method sets the active path in WSL to match the directory you’re working in from Windows. Here’s an example:
# create folder and go to it mkdir C:\temp\newfolder cd C:\temp\newfolder # enter wsl wsl
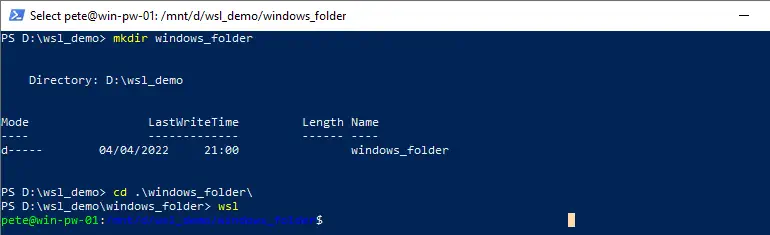
Once inside WSL, your default Linux distribution will start, and the working directory will be mounted at the corresponding path, in this case, /mnt/c/temp/newfolder. This is an efficient way to ensure your Linux session begins in a specific Windows directory.