Environment variables store key information on your system that programs can use to influence their behavior. For example, the AWS CLI uses the AWS_REGION variable to determine the region for API requests.
This guide will cover:
– Listing all environment variables
– Retrieving the value of a specific environment variable
– Setting or updating environment variables
1. List All Environment Variables
To view all environment variables and their current values, use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet with the Env: drive. Alternatively, you can use its shorter alias gci:
# List all environment variables Get-ChildItem Env: # Alt cmdlet gci Env:
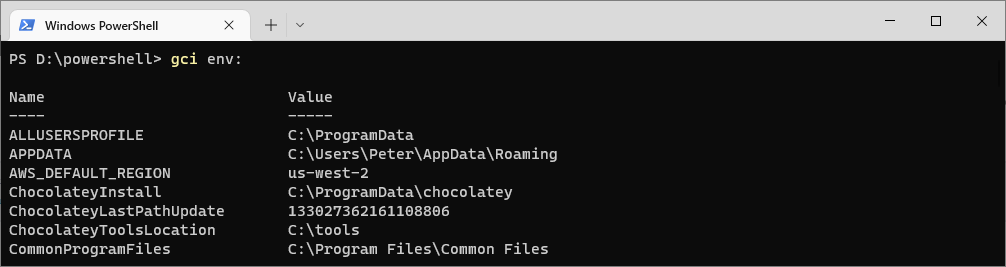
Both commands will display a list of environment variables along with their values.
2. Get the Value of a Specific Environment Variable
To return the value of a specific environment variable, such as AWS_DEFAULT_REGION, you can use one of these methods:
# Get the value of the aws_default_region environment variable gci Env:\AWS_DEFAULT_REGION # Do the same but alt (easier) syntax $env:AWS_DEFAULT_REGION
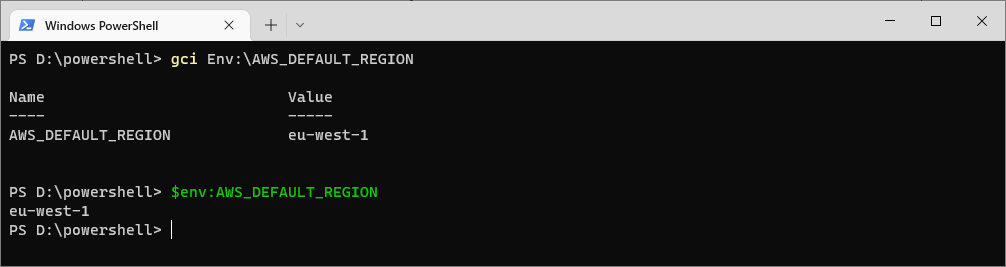
Both commands will output the value of the AWS_DEFAULT_REGION variable if it is set.
3. Set or Update an Environment Variable
To set or update an environment variable, assign a new value to it using the $env: syntax:
# Set the AWS Default Region Environment Variable $env:AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="eu-west-2"
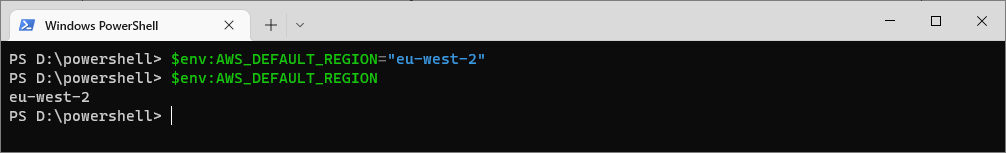
Important Notes:
– This change applies only to the current PowerShell session.
– To make the change permanent, you need to update the system or user environment variables in the Windows environment settings or use registry editing scripts.
For example, setting a permanent environment variable using PowerShell might involve modifying the registry:
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("AWS_DEFAULT_REGION", "eu-west-2", "User")
This approach ensures that the variable is available in future sessions.