In this blog post, we’ll go through the steps for using a PowerShell script that lists files in a directory along with their sizes and creation dates. This script is useful for disk space and for checking old files in a folder.
List Files with Size and Last Write Time
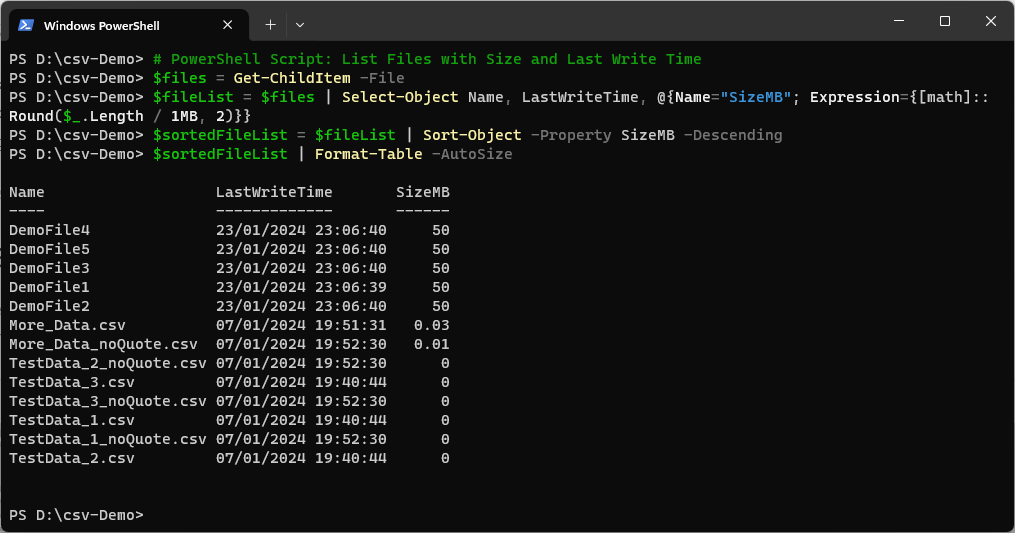
The following PowerShell script provides admins a quick overview of the files in the current directory, ordered by file size (MB) from highest to lowest.
PowerShell Script:
# PowerShell Script: List Files with Size and Last Write Time
$files = Get-ChildItem -File
$fileList = $files | Select-Object Name, LastWriteTime, @{Name="SizeMB"; Expression={[math]::Round($_.Length / 1MB, 2)}}
$sortedFileList = $fileList | Sort-Object -Property SizeMB -Descending
$sortedFileList | Format-Table -AutoSize
How It Works
> Get-ChildItem: Retrieves all files in the current directory using the -File parameter.
> Select-Object: Creates a custom object for each file with its name, last write time, and size in megabytes.
> Sort-Object: Orders the files by size in descending order.
> Format-Table: Displays the sorted file list in a table format.
Making It a Function
For better reusability, we can turn the script into a function:
# PowerShell Function: List-FilesWithSizesAndDates
Function List-FilesWithSizesAndDates {
param(
[string]$directoryPath = (Get-Location)
)
$files = Get-ChildItem -Path $directoryPath -File
$fileList = $files | Select-Object Name, CreationTime, @{Name="SizeMB"; Expression={[math]::Round($_.Length / 1MB, 2)}}
$sortedFileList = $fileList | Sort-Object -Property SizeMB -Descending
$sortedFileList | Format-Table -AutoSize
}
Example usage:
# List files in the current directory List-FilesWithSizesAndDates # List files in a specific directory List-FilesWithSizesAndDates -directoryPath "d:\mssql_backups"
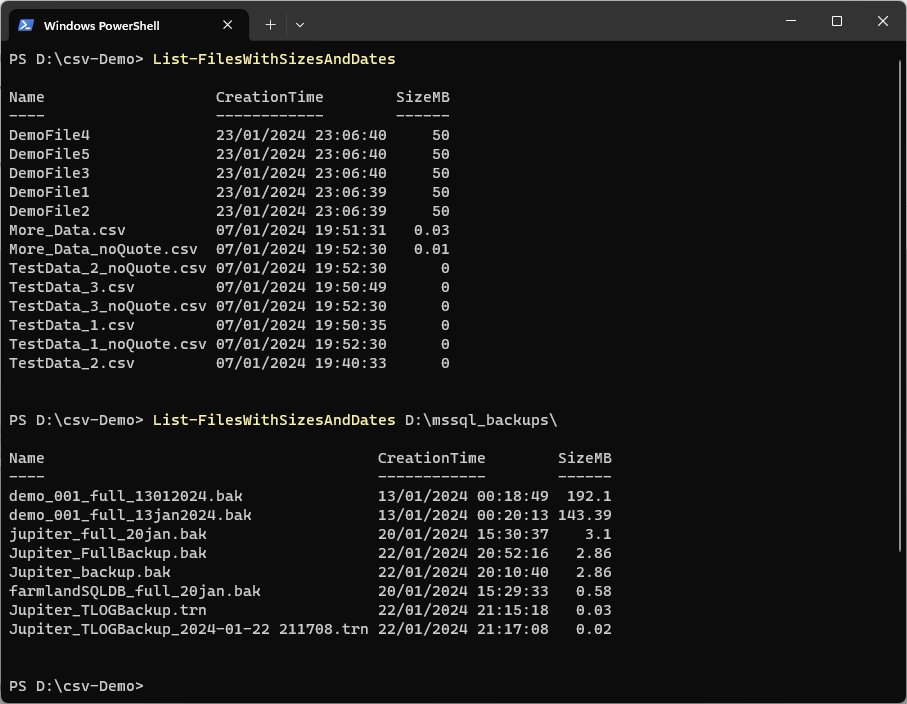
This function makes it easy to organize files by size and date, helping you quickly find large or old files that might need archiving or deletion. It’s also great for auditing, letting you track file creation dates for better record-keeping. Plus, you can name the function whatever you like, customizing it to fit your workflow and making your terminal experience even smoother.
Leave a Reply