This is my third Linked Server demo post, and this time, we’re connecting to a MySQL database.
Here’s a simple diagram of the setup covered in this post, configuring a Linked Server to a MySQL Database:
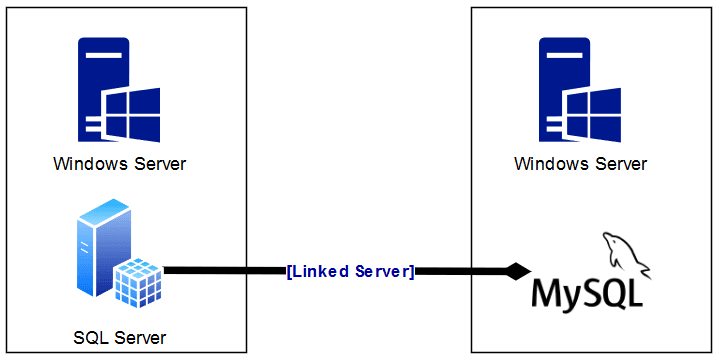
For this setup, I’ve covered it all in previous blog posts:
– Installing SQL Server on Windows
– Installing MySQL on Windows
– Testing Connectivity to Remote Database Server Ports
All of the above are necessary prerequisites for configuring this MySQL Linked Server. You could run on Linux for both MySQL and SQL Server (as from SQL 2017), but for this demo I’ve gone with a Windows Server setup.
The following is included in this guide to setup a Linked Server to MySQL:
Step 1: Create MySQL Linked Server Login
Step 2: Configure ODBC Data Source Settings
Step 3: Create a Linked Server to a MySQL Database
Step 4: Verify MySQL Linked Server Connectivity
Step 1: Create Linked Server Login on MySQL
You can create a MySQL user either through MySQL Workbench or via the command line. For this demo, I’ll use the MySQL CLI.
1. First, connect to MySQL:
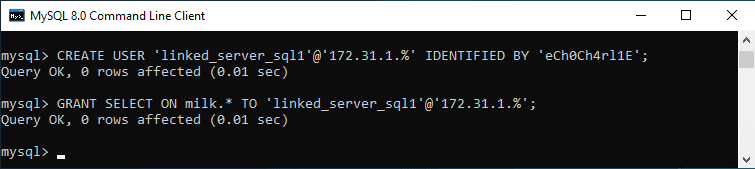
2. Create MySQL User with Permissions
In the example below, I’m creating a user and GRANTING SELECT capabilities for all tables within the database.
-- Create Linked Server user CREATE USER 'linked_server_sql1'@'172.31.1.%' IDENTIFIED BY 'eCh0Ch4rl1E'; -- Grant SELECT on all tables in milk from specific user subnet GRANT SELECT ON milk.* TO 'linked_server_sql1'@'172.31.1.%';
This grants read-only access to all tables in the milk database for connections coming from the 172.31.1.0 network range. If testing locally, replace 172.31.1.% with localhost.
If I want to test this new MySQL login locally, I can create the user using ‘localhost’ too. Below I’m opening the mysql.exe file rather than using the MySQL Command Line app which logs in as root.
Now querying the database I want as part of the Linked Server:
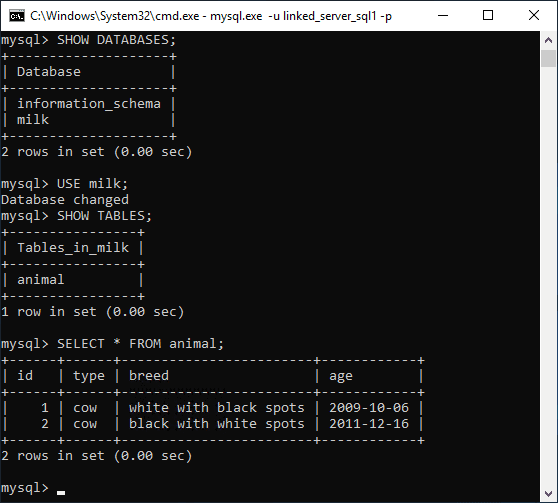
I only wanted read-only access, which I can confirm with a quick write test.
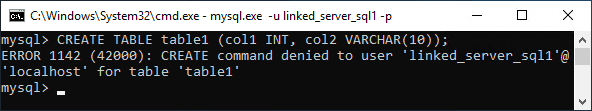
We could have also done this testing by logging in via MySQL Workbench.
That’s our Linked Server MySQL login tested and ready!
Step 2: Configure ODBC Data Source on SQL Server
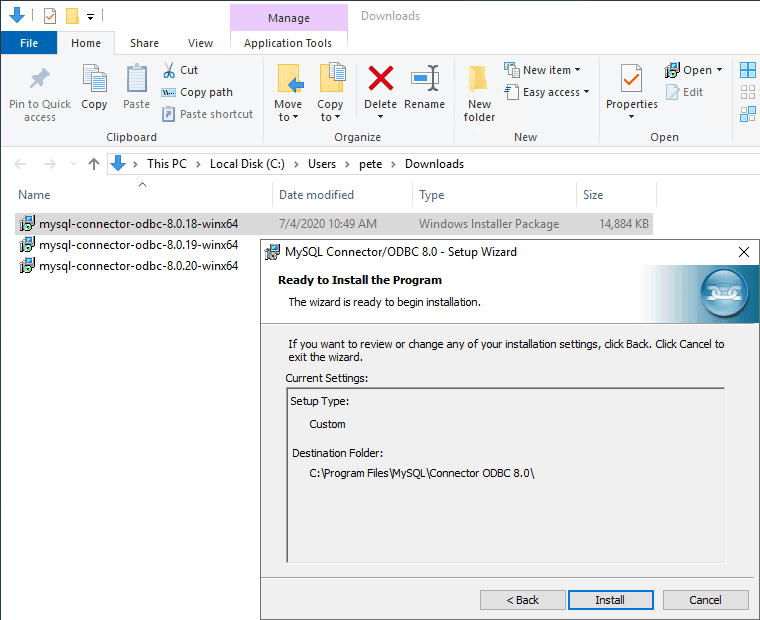
1. Download & Install MySQL ODBC Driver
The latest MySQL ODBC driver can be found here.
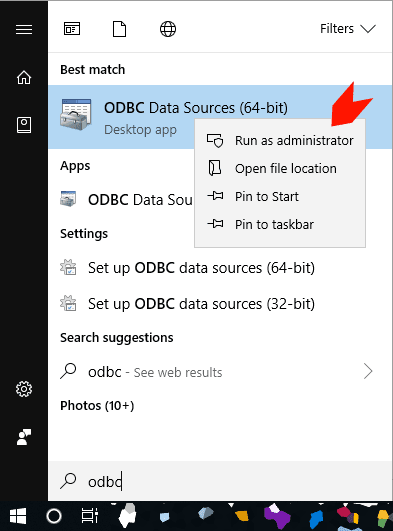
2. Run ODBC Data Sources as Administrator.
3. Navigate to the System DSN tab and click Add.
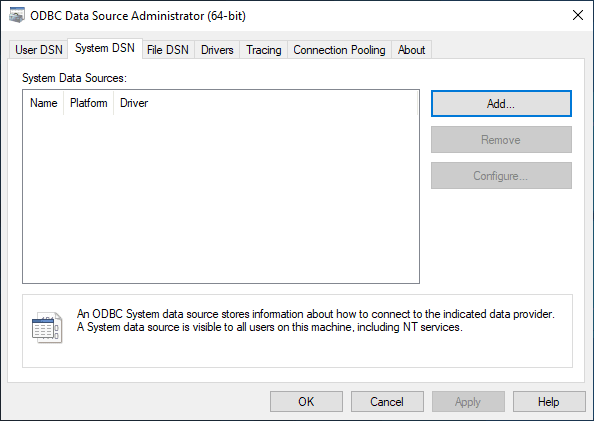
4. Select MySQL ODBC Unicode Driver.
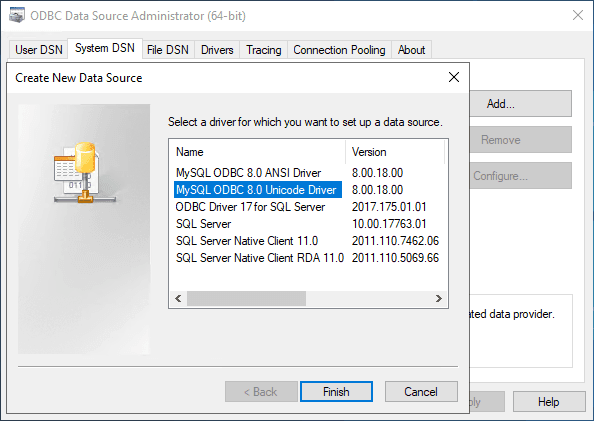
5. Enter the connection details:
– Server: MySQL_IP_or_ServerName
– User: MySQL_LinkedServer_Login_01
– Password: SecurePassword123
– Database: DatabaseName01
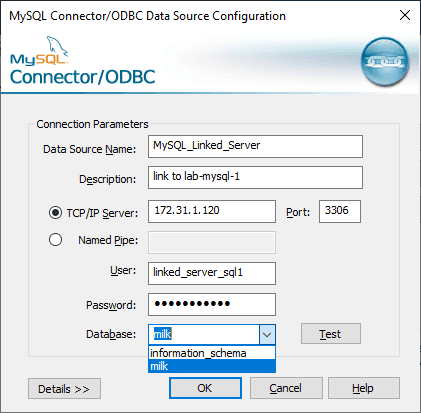
6. Click Test to ensure successful connectivity, then click OK.
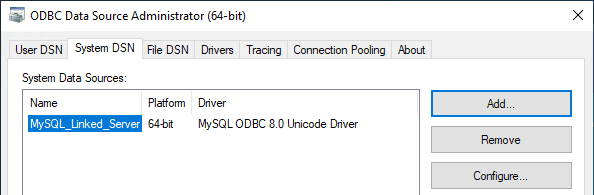
Step 3: Create Linked Server in SQL Server
1. In SSMS, expand Server Objects, right-click Linked Servers, and select New Linked Server.
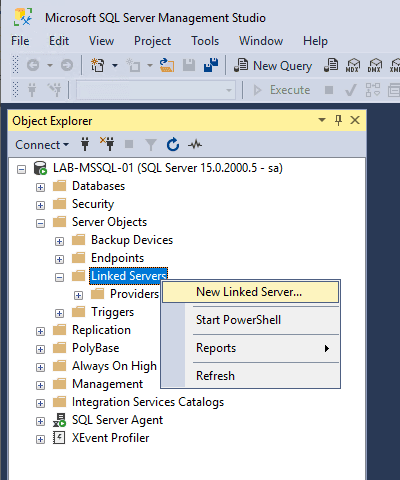
2. Configure the following:
– Linked Server Name: Choose a meaningful name (e.g., MYSQL_SERVER_1).
– Provider: Select Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers.
– Data Source: Enter the ODBC Data Source name configured earlier.
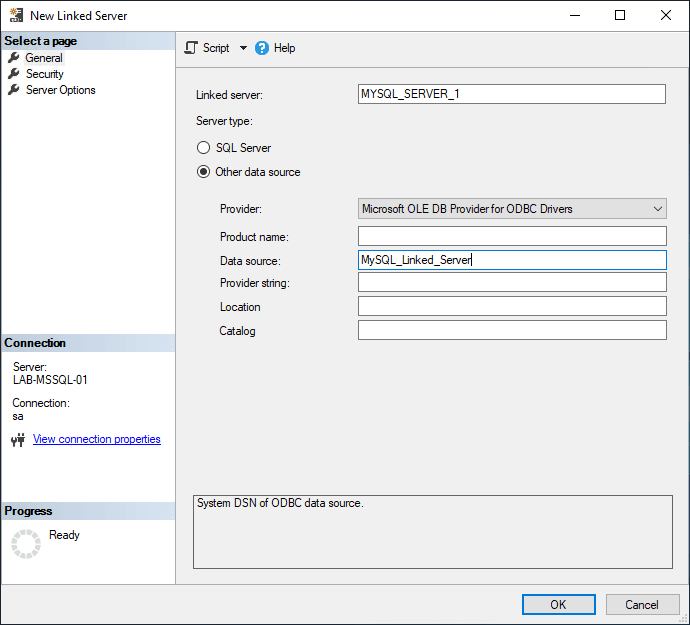
3. Under Security, enter the MySQL login details created earlier.
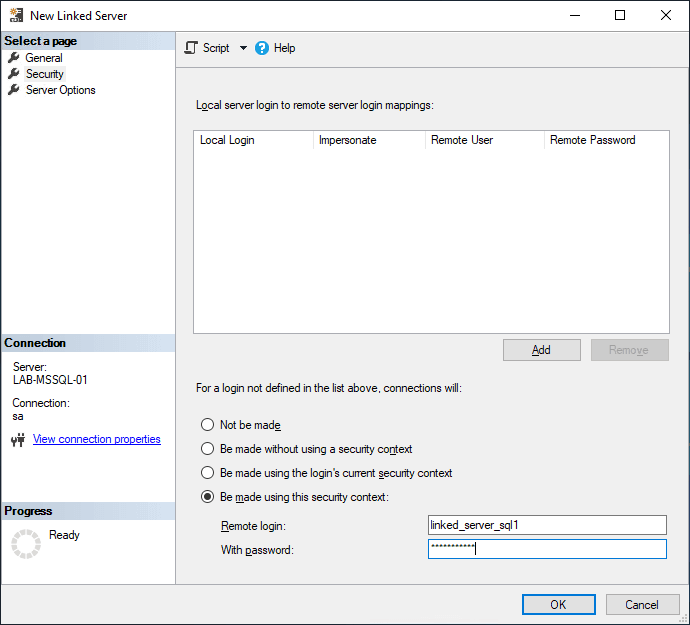
4. Leave Server Options as defaults.
Before we proceed and create this Linked Server, we can script out the Linked Server creation:
USE [master] GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'MYSQL_SERVER_1', @srvproduct=N'', @provider=N'MSDASQL', @datasrc=N'MySQL_Linked_Server' USE [master] GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname = N'MYSQL_SERVER_1', @locallogin = NULL , @useself = N'False', @rmtuser = N'linked_server_sql1', @rmtpassword = N'eCh0Ch4rl1E' GO
Once ready, execute the script or click OK in the Linked Server configuration window.
Step 4: Verify Linked Server & Run Queries
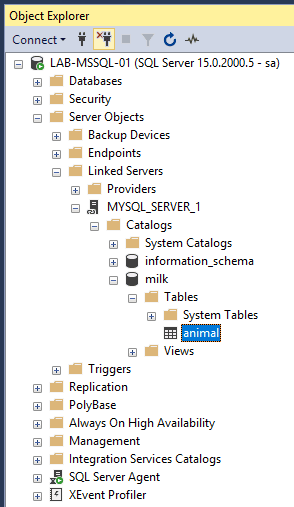
1. Check Linked Server in SSMS
– In SSMS Object Explorer, navigate to Server Objects → Linked Servers.
– Expand the new Linked Server and browse the database objects.
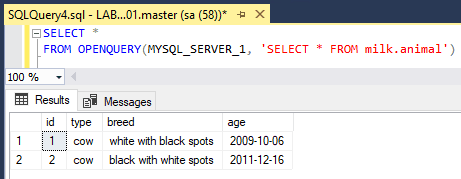
2. Query MySQL Database Using OPENQUERY
The query below executes against MySQL from SQL Server. If everything is configured correctly, you should see your test data.
-- MySQL Linked Server Example Query SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(MYSQL_SERVER_1, 'SELECT * FROM milk.animal');
Checkout the MS Docs for more information on OPENQUERY.
I hope this configuration guide was a good one for you, and you got SQL Server setup with a Linked Server to your MySQL Server.
If you have any troubles along the way feel free to comment below and I’ll try help!
Leave a Reply